Data analytics can immensely impact and improve a business’s decision-making processes. From better strategies to profits, explore the full scope of analytics.
Have you ever been in a meeting, witnessing crucial choices being based purely on gut feelings? While there’s merit in intuition, today’s intricate business ecosystem demands more. Across the globe, companies are wondering, “How does data analysis integrate into our decision-making process?” Grasping and utilizing the intricacies of informed “decision-making in business management” through data analytics might very well distinguish thriving enterprises from those struggling to keep up.
According to a study conducted by Deloitte, nearly half of the participants, tallying up to 49%, expressed the belief that analytical tools enhanced their decision-making prowess. In this article, we will explore the role of data analytics for today’s businesses and how analytics can help businesses make better decisions.
The Data Revolution in Today’s Business Landscape
Think of data analytics as the heartbeat of modern business intelligence. It’s analogous to piecing together a jigsaw. Individual data fragments might seem inconsequential, but combined, they weave a narrative, spotlighting customer behaviors, driving informed decisions, and occasionally, hinting at future trends. It’s not merely about crunching figures; it’s deciphering the tales they narrate.
The Genesis of Big Data:
Wondering where this avalanche of information originates from? That’s the realm of “big data”. There was a time when data analytics was a niche domain, mostly navigated by tech giants and affluent enterprises. It was a feather in a company’s cap but not foundational. Times have evolved. With tech democratization and intensifying market rivalry, data interpretation has transitioned from being a luxury to a cornerstone for businesses of every scale.
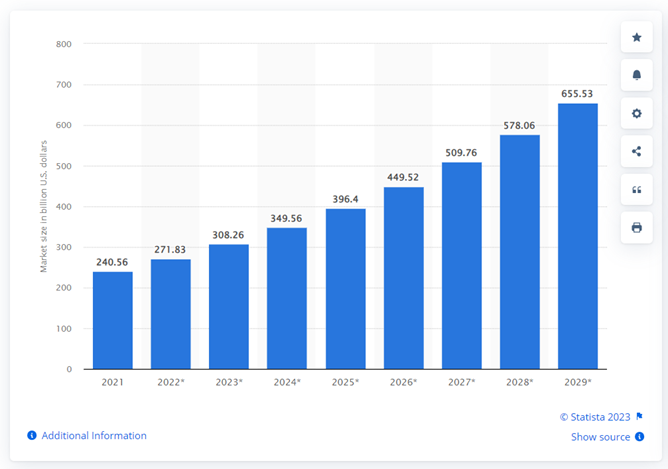
According to recent reports, over the next few years, the big data market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, with projections of over 650 billion dollars by 2029 from 240 billion dollars in 2021.
Our everyday activities, from online shopping sprees to casual internet surfing, began churning out data trails. However, the sheer volume of data causes an issue. The existing toolkits at the time were ineffective and could only either process a small amount of data at a time or take a very long time to do so, making the process lengthy and inefficient. This predicament spurred innovation, turning this data deluge from an impediment into a goldmine of possibilities. From understanding consumer behaviors to anticipating industry shifts, the use of data analytics has started shaping strategies and decisions.
Analytical Tools and Techniques
The top analytical tools that stand out are platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and SAS. Let’s look closely at what they do:
- Tableau: Emerging at the forefront of visual data interpretation, Tableau offers user-friendly dashboards that enable companies to sift through and comprehend their data reservoirs. Its easy-to-grasp interface democratizes data understanding, making it accessible to a wider audience. By amalgamating data from diverse sources and forming intricate visual representations, it offers firms a detailed peek into their operations and consumer landscapes.
- Power BI: As Microsoft’s contribution to the analytics domain, Power BI emphasizes real-time data processing. Leveraging its cloud-centric infrastructure, corporations can oversee their functions via live panels, craft extensive reports, and distribute key findings throughout their network effortlessly. Its tight-knit integration with other offerings from Microsoft, notably Excel, ensures that data remains interconnected across tools.
- SAS: An anchor in the realm of evolved analytics, SAS presents a suite of functionalities for data orchestration, visual interpretation, and insights powered by artificial intelligence. Rooted in statistical methodologies, it equips corporations with models that forecast future trends, allowing them to not merely respond to market shifts but also to shape them actively.
The Role of a Business Intelligence Analyst
Not only tools, but specific roles need to be assigned in organizations to be able to navigate data analytics into specific strategic decisions. This is mediated by a critical entity, known as the “business intelligence analyst.” These individuals function as the conduit between unprocessed data and tactical business maneuvers. Their skill resides in deconstructing complex data assemblies, ensuring the insights extracted are in concordance with the company’s aspirations. They customize the analytical tool’s functionalities to meet their organization’s specific needs, certifying the maximum utility of every data unit.
The Integration of Data Analysis in Business Domains
- E-commerce: Virtual retail entities are increasingly dependent on analytical strategies to individualize consumer interactions. Scrutinizing variables such as navigational habits, historical acquisitions, and consumer inquiries allows these entities to engineer bespoke product suggestions, enhance digital storefront configurations, and forecast forthcoming consumer predilections.
- Virtual Healthcare Services: The increasing traction of web-based health consultation platforms underscores the imperative for comprehensive studies. Utilizing data analytics can assist these platforms in monitoring aspects such as user interactions, drug consumption patterns, and subsequent responses. The chief objective of this initiative is to elevate the caliber of medical attention given to individuals in digital domains, harmonizing appointment mechanisms, and refining the user experience.
- Fintech: Digital finance portals harness analytical procedures to fortify investment advisories, identify duplicitous endeavors, and craft tailored fiscal instruments. Through a detailed inspection of expenditure trends, market oscillations, and client feedback, these platforms can fine-tune their service repertoire and bolster protective measures.
- SaaS Enterprises: Businesses in the Software as a Service sphere capitalize on data scrutiny to gauge client interaction with their digital offerings, pinpoint high-value functionalities, and recognize potential enhancements. Analyzing utilization trends, iterative feedback, and engagement indicators is pivotal for cyclical product optimization.
Advantages of Data Analysis
- Customized Interaction Paradigms: Analytical insights afford digital businesses the luxury of deciphering distinctive user predilections, and facilitating the customization of content, commodities, or assistance correspondingly.
- Proactive Analytical Forecasting: By foreseeing client necessities, market realignments, and nascent inclinations, digital enterprises can perpetually maintain a vanguard stance in their propositions.
- User Engagement Amplification: Comprehending the catalysts behind user captivation enables platforms to hone their substance and structural design, fostering maximal user allegiance.
- Marketing Endeavor Refinement: Initiatives grounded in data-derived cognizance assure that promotional activities are concentrated, germane, and yield superior investment returns.
- Threat Containment Protocols: In the virtual arena, perils such as cyber intrusions or deceptive acts are more predictably neutralized through astute data analytical practices.
- Informed Digital Product Evolution: Continuous product and service refinement in the digital space leverages instantaneous feedback and behavioral analytics from users.
- Conversion Optimization Strategies: Discerning and reacting to behavioral archetypes enables digital establishments to fortify their consumer procurement funnel, driving enhanced transactional outcomes.
Data Management: Essential Foundation for Analytics
Within the intricate sphere of data analytics, a fundamental truth persists: without rigorous “data management,” even the most cutting-edge analytics can guide more towards confusion than clarity. The significance of the way data is assembled, stored, and retrieved is analogous to the importance of a robust foundation for a high rise. If the base is compromised, the entire structure, regardless of its aesthetics, is susceptible.
The realm of data management is both broad and complex. Here’s a closer look at its key elements:
- Storage: It’s not merely about allocating space for accumulating extensive data. It involves guaranteeing that the storage facility is capable of expansion, durability, and security. As enterprises expand, they generate more data. Revolutionary solutions like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage provide businesses with the ability to scale without investing in substantial physical data warehouses.
- Retrieval: Efficient data management transcends storing information; it encompasses the ability to extract it promptly and effectively when necessary. Tools like MySQL and MongoDB have changed the landscape of data access, offering structured approaches that enhance speed and efficiency. The pace at which data is accessed can directly influence the agility of decision-making processes.
- Cleaning: Unprocessed data is frequently disorganized and cluttered. It could contain redundancies, contradictions, or outright errors. Rigorous data cleaning guarantees the dependability of data. Various manual or automated strategies are employed to sift through datasets, ensuring uniformity and accuracy. This stage, although demanding, is pivotal for the success of subsequent analytical processes, as analytical algorithms are only as efficient as the data they process.
Data Management & Decision-Making:
The intertwined nature of data management and decision-making is unmistakable. Consider a scenario where a decision-maker, perhaps a CEO, bases a strategic decision on analytics derived from flawed data. The outcome, regardless of the decision’s rationale, could misdirect the organization. This underscores the necessity for robust data management protocols. The “analysis of data” is heavily dependent on its quality, upheld through comprehensive data management practices.
Challenges and Considerations in Data Analytics
Challenges
- Concerns Over Data Integrity:
- Applicability: Filtering the data ocean to pinpoint germane pieces is a task fraught with challenges.
- Precision: Inaccuracies in datasets can spin a web of misinformed inferences. Hence, it’s paramount to establish stringent vetting mechanisms.
- Currentness: Decisions based on stale information can deviate from the real-time pulse of the marketplace.
- Decoding Data Rightly:
- Evading Biased Views: A lurking challenge is the tendency to perceive data through the lens of preconceived notions.
- Balancing Tech with Touch: While technology streamlines the analytics, it’s vital to ensure the human touch remains, capturing the subtleties that machines might miss.
Considerations
- Navigating Ethical Landscapes:
- Openness in Gathering: Businesses ought to elucidate their methodologies and intents behind data accumulation.
- Safeguarding Information: With cyber threats on the rise, fortifying data reservoirs against potential breaches becomes indispensable.
- Respecting Individual Spaces: It’s a cardinal duty to cherish and uphold the privacy sanctum of individuals, especially when their personal details are at stake.
- Being Aware of Changes:
- Persistent Evolution: Data insights exist in a dynamic ecosystem where ongoing development is required to keep up.
- Adapting to Tool Progressions: Modern data analysis methods are a necessity for any successful organization.
- Upholding Gold Standards: Data must be managed in the most effective, efficient, and well-informed way possible, thus staying up-to-date on best practices is essential.
Conclusion
In the nexus of business and advancing technology, it’s unmistakable that contemporary trailblazers capitalize on the robustness of analytical insights derived from extensive data. Success now hinges on extracting nuanced intelligence from data rather than simple intuitive judgment, propelling actionable, strategic frameworks.
Nonetheless, this path comes with its unique set of trials encompassing the maintenance of data integrity, navigating the intricacies of confidentiality, and adapting to the continuous evolution within the analytical instrumentation.
The shift towards a paradigm rooted in data transcends operational change; it’s a core strategic metamorphosis influencing a company’s competitive trajectory and resilience. Fundamentally, neglecting the critical pivot toward a data-anchored methodology doesn’t merely represent an oversight—it risks undermining the enterprise’s enduring relevance and prosperity.





